2023 April Freeze Effect on Corn and Soybean
Chad Lee, Conner Raymond, and Carrie Knott
University of Kentucky
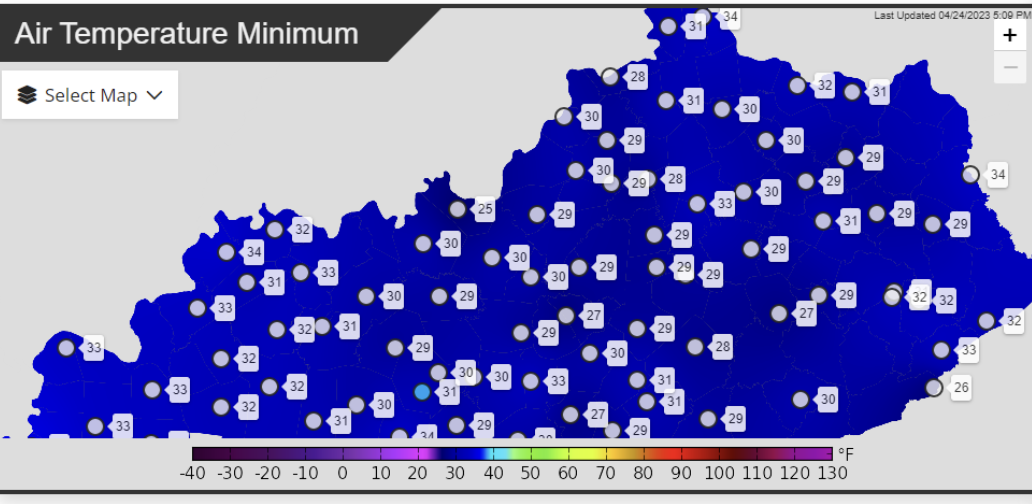
Freezing temperatures were recorded across Kentucky Monday morning, April 24, 2023. The coldest temperatures were mostly in central and eastern Kentucky, but freezing temperatures were as far west as Trigg and Webster counties. Temperatures fell to or slightly below freezing in the following counties from Sunday to Monday: Butler, Caldwell, Carroll, Christian, Crittenden, Graves, Grayson, Hardin, Logan, Meade, Ohio, Taylor, and Webster counties (Table 1, at the end of this article). Webster and McLean County were the coldest at 30°F. Frosts likely occurred west of these counties. The good news is that soil surface temperatures likely stayed in the low 50’s to mid-40’s. This is based on soil surface temperatures measured at UKREC in Princeton, KY.
About 36% of corn acres and 20% of soybean acres were planted as of April 23, 2023, according to the USDA-NASS.
Figure 1. Kentucky Mesonet recordings of lowest air temperatures since midnight April 24, 2023.
Corn and Soybeans at Risk
Corn and soybeans are at more risk to death from the freeze events at specific growth stages and in certain conditions. The following scenarios go from greatest risk to least risk of plant death from the freeze events.
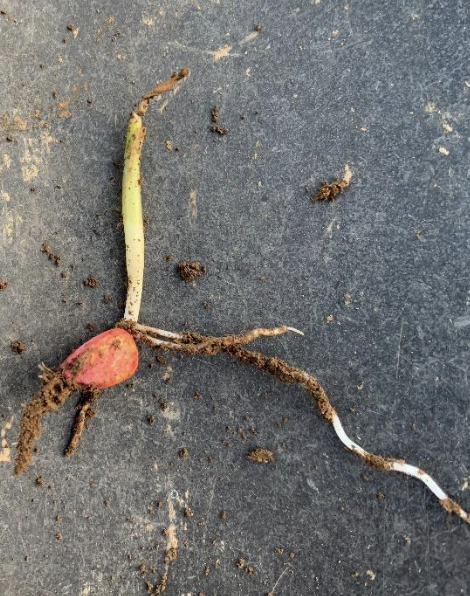
Soybeans at the “crook” stage where the stem is emerged and bent over like a shepherd’s crook were the most susceptible to the freeze (Figure 1). These plants were most likely to be killed by the freeze or frost. At crook stage, typical damage is along the stem with some yellowing of the cotyledon. This will be followed by plants snapping off where damage was observed (Figures 2 and 3).
Figure 2. Soybean plants at the ‘crook’ stage. Stems are fully exposed, but cotyledons have not moved above soil surface yet. (Soybean images by Conner Raymond and Carrie Knott)
Figure 3. Early signs of freeze damage observed on a soybean plant after 3-4 days of active growth. When freeze damage occurs at crook stage, yellowing of cotyledon and stem damage are visible. (Soybean images by Conner Raymond and Carrie Knott)
Figure 4. Final stage of crook freeze damage to plant appears after 7-10 days of active growth. Top portion of plant has broken off at site of damage (Soybean images by Conner Raymond and Carrie Knott)
Corn and soybean seeds and seedlings in furrows that were not fully closed are at risk of being killed by the freeze.
Corn or soybean seeds that were planted shallow had a slight risk of freeze damage, although plant death from the freeze is unlikely.
Corn plants emerged may have tissue above the soil surface die off from the freeze, but the growing points should have been insulated beneath the soil surface. Those corn plants should recover well. No yield loss is expected.
Figure 5. Emerged corn seedling with freeze damage at the very top of the emerged seedling, but no damage closer to the soil surface or below it. (Image by Chad Lee)
Soybean plants that have FULLY emerged and are at the VE growth stage (emergence) should survive the freeze event, based on observations during freeze events in late April 2021 and early May 2020. If the soybean cotyledons survive, the soybean plants will survive, and no yield loss will occur. If the cotyledons do not survive, the plant will not survive, either.
Corn and soybean seeds at proper planting depths are at very little risk from the freeze. Corn and soybean radicles (the shoots emerging from the seeds) that are still below the soil surface likely were insulated and will survive.
We need about 5 days of warm weather before symptoms are easy to see. Based on current forecasts, it may take six or seven actual days to get the 5 days of good growing conditions. Plants or plant parts that have turned black or brown and have lost turgor pressure are easy to identify.
Corn plants need to be examined from the seed upward. We are assuming that the roots are deep enough to not be a concern. Dig up some corn plants and look for any signs of brown/black areas from the seeds upward. If plants are white to yellow beneath the soil and turgor pressure is good, then the seedlings are likely to survive.
Maybe Just a Chill
Corn and soybean seeds that are in the process of germinating during the freeze are at risk of taking in cold water (imbibitional chilling) within the first 24 to 48 hours after planting. If the soil temperatures were below 50F for an extended period during those 24 to 48 hours, then the seeds are more likely to be damaged. There is some debate about how long the soils need to stay below 50F before severe damage is done from the imbibitional chilling. We can say those seeds are at risk. At this point, either the seeds were damaged, or they were not from imbibitional chilling. Emergence will be slower in these fields. The fields can be scouted in about five days or so to determine the health of germinating seeds and/or emerged plants.
Table 1: Low temperatures recorded across the state from 4/21/23 through 4/24/23. Freezing temperatures are highlighted in light blue. Weather data from the Kentucky Mesonet.
Resources
Coulter, Jeff. 2021. Spring Freeze Injury in Corn. University of Minnesota Extension. https://extension.umn.edu/growing-corn/spring-freeze-injury-corn
KY Climate Center. 2023. Kentucky Mesonet. https://www.kymesonet.org/ accessed April 24, 2023.
Lee, C.D. Evaluating early season frost damage to corn. AGR-192. Univ. of Kentucky Cooperative Extension Service. http://www2.ca.uky.edu/agcomm/pubs/agr/agr192/agr192.pdf
Nielsen, R.L. 2020. Assessing Frost/Cold Temperature Injury to Young Corn. Corny News Network. http://www.kingcorn.org/news/timeless/FrostedCorn.html
Nielsen, R.L. 2020. Cold Soils & Risk of Imbibitional Chilling Injury in Corn. Corny News Network. Purdue Univ. https://www.agry.purdue.edu/ext/corn/news/timeless/ImbibitionalChilling.html
Staton, Michael. 2021. Assessing frost/freeze damage to emerged soybeans. Michigan State University Extension. https://www.canr.msu.edu/news/assessing-low-temperature-injury-to-soybeans
Taylor, M., A. Nygren, J. Rees., J. Specht and A. Timmerman. 2020. Evaluating freeze and chilling injury in corn and soybeans. Nebraska Cropwatch. https://cropwatch.unl.edu/2020/evaluating-freeze-and-chilling-injury-corn-and-soybeans
USDA-NASS. 2023. USDA-NASS. Crop Progress and Condition. https://www.nass.usda.gov/Statistics_by_State/Kentucky/Publications/Crop_Progress_&_Condition/cw23/CW042423.pdf